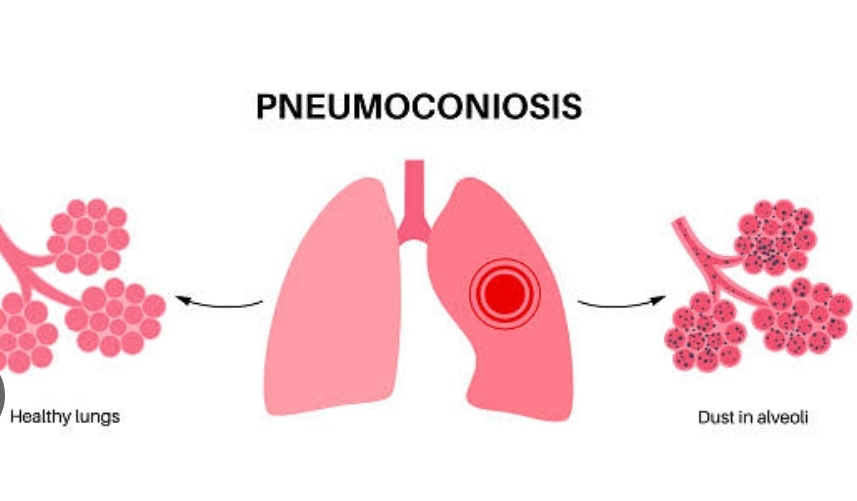
PNEUMOCONIOSIS
Pneumoconiosis is a general term for a group of lung disease caused by inhalation and retention of dust particles.
Hazardous effect of dusts depends on-
1.Chemical composition
2.Concentration of dust in the air
3.Period of exposure
4.Health status of person exposed
As no cure for the pneumoconiosis is known, it is essential to prevent these diseases from arising.
Types of dust causes pneumoconiosis
1.Inorganic dust
Coal - Anthracosis
Silica - Silicosis
Asbestos - Asbestosis, cancer of lung
Iron - Siderosis
2.organic dust
Cane fibre - Bagassosis
Cotton fibre - Byssinosis
Tobacco - Tobaccosis
Grain dust - Farmers lung
(A).SILICOSIS
Silicosis also known as Grinder's Disease.
Most common pneumoconiosis in the world First reported in Kolar Gold Mines (KGF)
Caused by - Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂)
Occupation-mining industries (gold, silver, etc.), sand blasting
Causes alveolitis Nodular Fibrosis
Mainly affects-upper zone of lung
Types of silicosis
1.Acute silicosis
2.Asymptomatic silicosis
3.Accelerated silicosis
4.Chronic silicosis
Symptom
Dyspnea
Tachycardia
Loss of appetite
Chest pain
Fever
Auscultation reveals ronchi sound
Diagnostic evaluation
1.History collection
2.Physical examination
3.Chest x- ray -Snow Storm appearance
4.CT scan
Management
1. Antibiotics and antihistamine drugs
2.Chest physiotherapy
3.oxygen administration to avoid hypoxia.
4. Bronchodialator to improve breathing
Preventive measures:
1.Rigorous dust control measures
e.g. personal protective equipment, masks or respirator with mechanical filters or with oxygen substitution, hydroblasting.
2. Regular physical examination of workers
Complication
Cyanosis
Cor pulmonale
Respiratory insufficiency
Susceptible to Silicotuberculosis
Chronic bronchitis
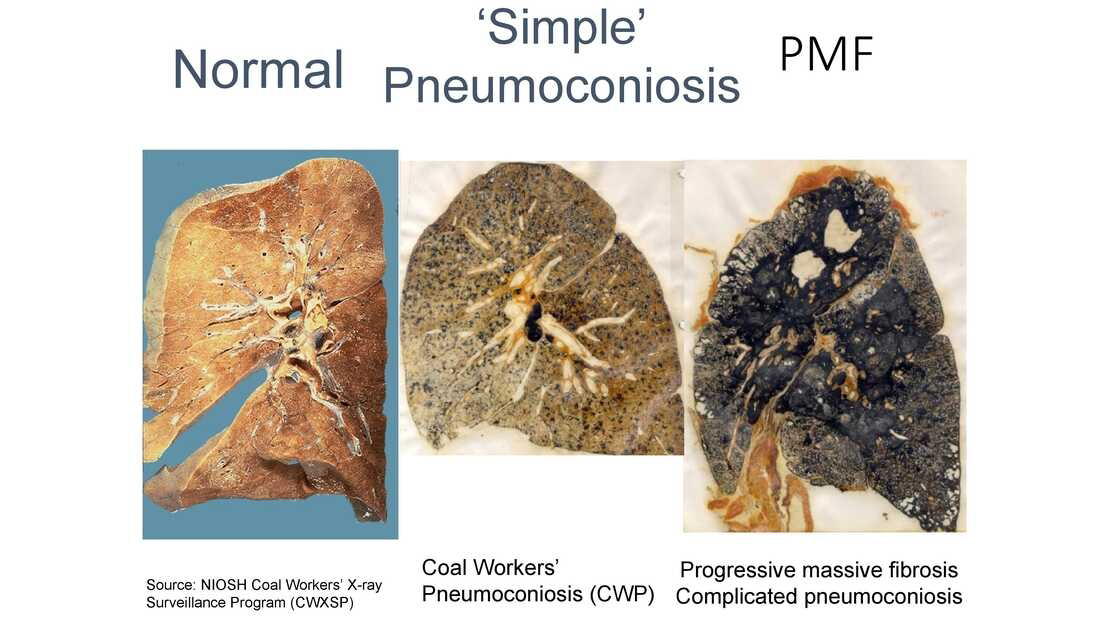
(B) .COAL WORKERS PNEUMOCONIOSIS (ANTHRACOSIS) :-
Coal worker pneumoconiosis is defined as the disease of the lung resulting from chronic exposure to coal dust, it's inhalation and deposition and the tissue reaction of the host to it's presence.
Also known as Black Lung/Coal miner's pneumoconiosis
Exposure - 10 years
Types
1.Simple coal worker pneumoconiosis :- it is characterized discrete macules of dull of due in the upper zones of ling but little ventilatory impairement, this phase may require above 12 years work exposure for its development.
2.Complicated coal worker pneumoconiosis/ Progressive massive fibrosis:- This phase is characterized by large fbrotic massess consiting of coal dust and collagen in upper and middle zones of lung and severe respiratory disability, frequently resulting in premature death.
Clinical manifestations
1.Shortness of breath
2. Weight loss
3.Fever
4.Fatigue
Diagnostic evaluation
1. Occupational history
2. Physical examination
3. Pulmonary function test :- decrease total lung capacity
Complication
1. Pleural effusion
2. Cor pulmonale
3. CCWP(Coal worker pneumoconiosis) +RA(Rheumatoid arthritis) = Caplan syndrome
Control measures :-
Prevention is the best especially as stoppage of further exposure , dust control at coal face,
Environmental monitoring and personal protection , periodic medical examination.
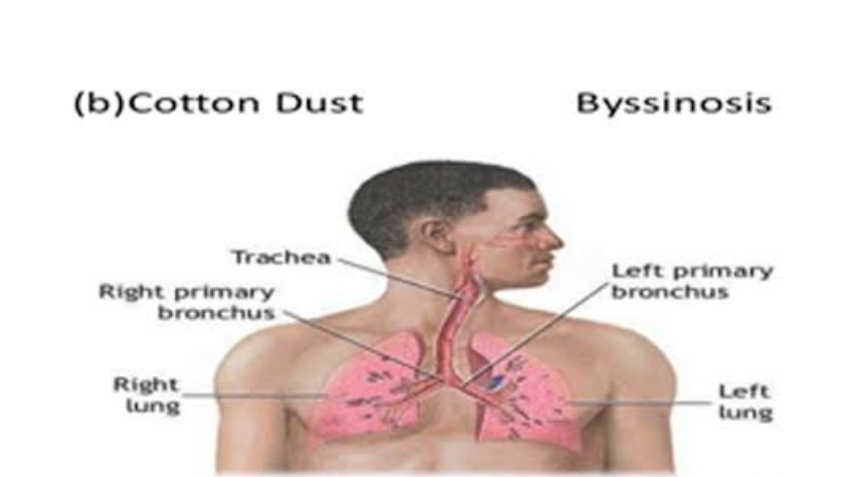
C. BYSSINOSIS :-
Byssinosis also called brown lung is an occupational lung disease caused by exposure cotton dust in inadequately uncontrolled working environment.
Also known as Monday chest tightness/Monday morning fever/ Mill fever
Occupation-Textile industries
Clinical manifestation :-
1.Tightness of chest
2.chronic cough
3.Progressive dyspnea
Diagnostic evaluation
History collection
Physical examination
Chest x-ray
CT scan
Management
1. Avoid exposure to harmful dust.
2.Bronchodialators helps to relieve mild to moderate symptoms .
3.Corticosteroids helps to reduce swelling
4. Oxygen therapy
5.Nebulisation
6.Breathing exercise
Prevention
1.Properly use personal protective equipmemts
2.Avoid smoking
Complication
Respiratory failure
Chronic bronchitis
Emphysema
D. BAGASOSSIS
Caused by-Sugarcane dust (bagasse) / Molasses.
Agent- Thermoactinomyces sacchari
It was first reported in India by Ganguli and pal in 1955 in a cardboard manufacturing farm near Kolkata.
Exposure :- 2-4 months
Clinical manifestations
Loss of appetite
Weakness
Breathlessnes
Cough with sputum
Fever with chills
Chest pain
Diagnostic evaluation
History collection
Physical examination
Chest X-Ray
Management
Medical management
Antitussive, Antipyretics , Fluid rehydration , rest and nutrition and oxygen supplementation may be required for the symptoms and control managment.
Qa
Preventive and control
1. Measure for the prevention and suppression of dust as wet process
2. Personal protective equipment
3.Period medical check up for worker
4.Bagasse control - keeping the moisture content below 20% and use of propionic acid
Complication
Diffuse fibrosis
Emphysema
Broncheietasis
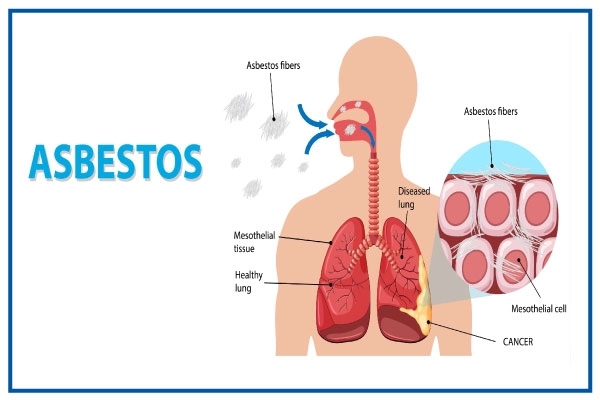
(E) ASBESTOSIS
Asbestosis is a chronic inflammatory medical condition affecting the parenchymal tissue of the lung due to long heavy exposure to asbestos.
Occupation - Cement, Fireproof textile,Roofer
Clinical manifestation :-
Dyspnea on exertion
Decreased vital capacity
Coughing
Cyanosis
Cardiac distress
Diagnostic evaluation
History collection
Physical examination
Chest x-ray - Ground grass appearance
Complication
1.Lung cancer
2.Right side heart failure
Prevention :-
1.Use safer types of asbestos
2.Rigourous dust control
3.Periodic examination of worker, biological monitoring
4.Continuing research
(F) FARMERS LUNG
Farmer lung is defined as an occupational lung disease called by prolonged inhalation of hay or grain dust which contains thermophilic actinomycetes.
Clinical manifestation
Hypersensitivity pneumonia occurs
Malaise
Fever
Pulmonary fibrosis
Diagnostic evaluation
History collection
Physical examination
Chest x-ray
CT scan
Complication
Pulmonary fibrosis
Cor pulmonale
Preventive measure
Use of personal protective equipment e.g. Mask.
Reference :-
1.B. Venkatesan. Textbook of medical surgical nursing first edition. Published by Emess medical Publishers.











0 Comments