Bone Marrow Biopsy And Aspiration
Aspiration is defined as sucking a small amount of tissue in to the needle by applying suction with syringe.
Biopsy is defined as cutting and removing a small amount of tissue from an area for examination.
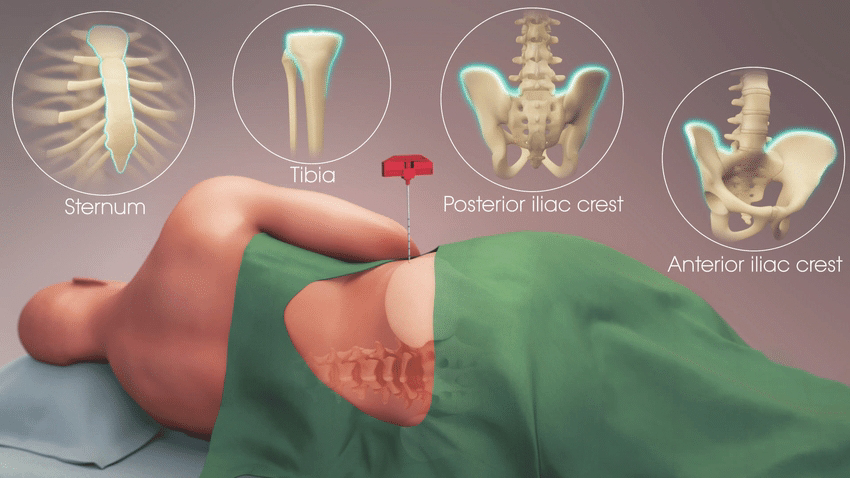
Bone marrow aspiration is a diagnostic procedure performed in blood dyscrasias in which a specimen of bone marrow is taken from the sternum, iliac crest posterior, superior iliac spine or tibia (children) by means of a hollow thick needle.
Purpose :-
1. To diagnose hematological disorders.
2. To diagnose metastatic neoplasm.
3. To determine the number, size and shape of red cells, white cells and platelets.
4. To follow course of disease and patients response to treatment.
5. To diagnose deficiency states of vitamin- biz, folic acid, iron, pyridoxine, etc
INDICATION :-
1.Diagnostic :-
Bone marrow examination is essential for the diagnosis of a plastic, megaloblastic anemia, multiple myeloma, myelofibrosis, myelosclerosis and aleukemic leukemia.
Bone marrow examination is helpful, but not essential for diagnosis of anemia, leukemia, thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytoma, tropical diseases, malaria, kala azar, etc.
2.Prognostic :-
Agranulocytosis, leukemia and anemia.
3.Therapeutic :-
Bone marrow transplant.
SITES AND POSITION OF THE PATIENTS :-
1.Sternal puncture: The usual puncture site is either the manubrium sterni or the upper part of the body of ster- num. The Patient lies in the dorsal recumbent position (supine) with a pillow under the shoulders to raise the chest.
2.Iliac puncture: The bone marrow biopsy is taken from the iliac crest 2 cm posterior and 2 cm interior to the anterior superior iliac spine. Alternately, the posterior iliac spine is also used. For iliac puncture, the patient lies either on his side or abdomen.
3.Spinous process aspiration: In the spinous process of the lumbar vertebrae, usually L3 or L4 is the puncture site. The patient is placed in the lumbar puncture position.
4.Tibial puncture in children: In children upto the age of 2 years the proximal end of tibia, just below the tibial condyless and medial to the tibial tuberosity is selected.
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
1. The procedure should be done under very strict aseptic technique, since the infection can be intro- duced into the bone cavity through the puncture site.
2. The penetration of the needle beyond the bone cavity is prevented by the guard attached to it.
3. The complications should be watched for injury to associate organs.
4. The vital signs should be checked throughout the procedure and reassure the patient.
5. The nurse should remain with the patient throughout the procedure and observe for signs of complications
6. Smear is made on 3 to 4 slides. Specimens are sent to the laboratory without delay.
ARTICLES
A sterile tray
1. Sponge holding forceps- 1
2. Dissecting Forceps - 2
3. Marrow puncture needle without obturator - 1
4. Aspiration syringe - 1
5. Syringe for local anesthesia -1 , needles -2
6.small bowls -2 , to take cleaning solutions
7. Cotton swabs, gauze pieces, cotton pads etc. In containers.
8. Dressing towels or slit to create a sterile field.
9 . Bard Parker (BP) handle with blade -1 , to make a small incision on the skin
10.Slides to make smears.
An unsterile tray :-
1. Mackintosh and towel
2. Lignocaine 2%
3. Adhesive tape and scissors
4. Kidney tray and paper bag
5. Spirit, iodine, tincture of benzoin etc.
PROCEDURE :-
1. Transfer the patient from bed to treatment room.
2. Position the patient and assess the doctor to locate and mark the site.
3. Open small dressing pack and slides, syringes, needles and scalpel blade the pack.
4. Assist the doctor to clean site with antiseptic solution and drape with sterile towels.
5.A small incision may be made with scalpel blade. Bone marrow needle with stylet is introduced through incision and marrow is aspirated.
6. Inform patient that a brief episode of sharp pain during aspiration will be experienced.
7. Syringe with aspirated marrow is handed over to technician and collect into various containers as indicated.
8. Collect bone marrow tissue in small bottle containing formalin-alcohol-acetic acid (FAA) solution.
9. Apply pressure over punctured site until bleeding ceases.
10. Assist doctor to seal punctured site with tincture of benzoin and by applying for dressing.
AFTERCARE :-
1. Keep the patient in supine or lateral position.
2. Allow the patient to rest for few hours after the procedure.
3. Check the vital signs and observe for signs and symptoms of complications.
4. The puncture site should be treated as a surgical wound. The dressing should be done under strict aseptic techniques.
5. Give mild analgesics if needed.
6. Label specimen and send to laboratory.
7. Replace the articles after cleaning
8. Wash hands.
9. Record the procedure in the nurse's record sheet.
COMPLICATION
According to the site are given below:
Sterna puncture: Injury to the pericardium, myocardium lungs and to the large blood vessels of the mediastinum.
Iliac site: Injury to the sacroiliac ligament, dural sac and Vertebral site: Injury to the dural sac and the spinal cord. cauda equina.
Tibial site: Injury to the tibial collateral ligament of the knee.
OTHER COMPLICATIONS
1.Bleeding from puncture site. The causes are thromo- cytopenia and bleeding diathesis. Bleeding can be prevented by local pressure.
2. Perfection of aorta, due to penetration of posterior side of sternum if too much force is applied.
3. Infection (osteomyelitis).










0 Comments